From Coal to Current: Electricity on the Titanic
Explore the history and technology of electricity on the Titanic. Learn about the ship's electrical systems and how they were used during its fateful voyage.

Did the Titanic have electricity? Yes, it did.
In fact, the Titanic was equipped with a state-of-the-art electrical system that powered everything from the ship's lights to its elevators.
In this article, we will explore the world of electricity on the Titanic, from its electric generators to the electrical engineers who maintained them.
The Power Heart of the Titanic: Its Electric Generators
At the core of the Titanic's operational prowess were its electric generators, sophisticated marvels of engineering that converted steam power into the electricity that lit up and powered the ship. Fueled by the steam generated from 29 boilers, the Titanic's energy infrastructure was a testament to the early 20th century's industrial advancements. The ship housed three main steam-driven dynamos, pivotal in generating the electrical current that coursed through the vessel.
These dynamos were not just any generators; they were specifically designed to handle the vast electrical needs of the Titanic, from illuminating over 10,000 light bulbs to powering the ship's innovative heating and cooling systems. Each dynamo had the capacity to produce a significant amount of electrical power, showcasing the monumental effort put into ensuring the Titanic was at the cutting edge of technology.
Positioned in the heart of the engine room, these generators were surrounded by a maze of pipes, gauges, and levers. The operation of the generators was a complex task, requiring constant attention and adjustments by the ship's dedicated team of electrical engineers. These professionals were tasked with the crucial role of monitoring the generators’ output, ensuring a steady and reliable supply of electricity to all parts of the ship.
The electricity generated by these dynamos was distributed throughout the Titanic via an extensive network of cables. This network was ingeniously designed to be both efficient and safe, with numerous safeguards in place to protect against electrical faults.
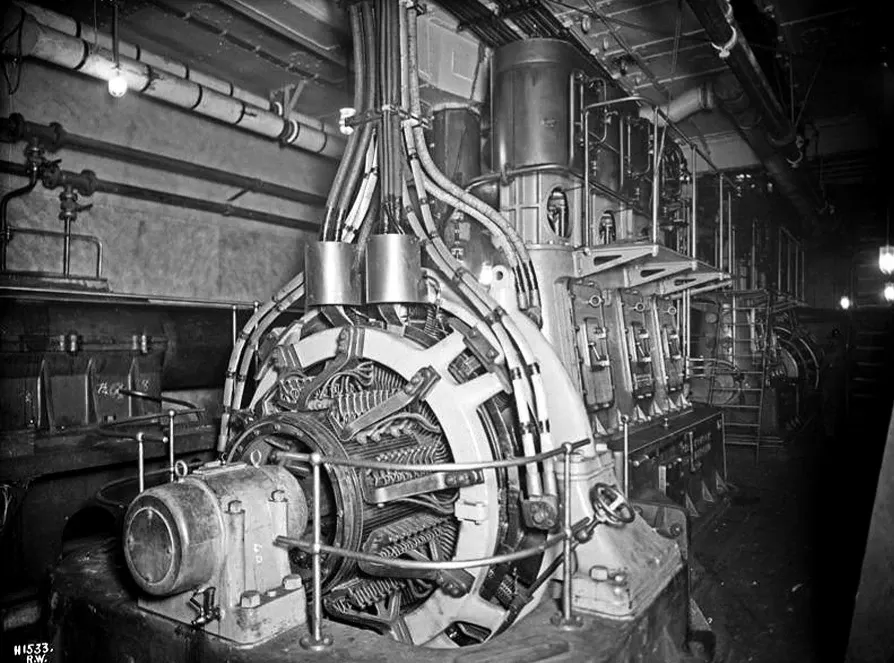
The ship's electrical system represented a harmonious blend of functionality and innovation, with the electric generators at its heart embodying the spirit of an era that believed in pushing the boundaries of what was possible. As the engines roared and the boilers steamed, the dynamos quietly ensured that the Titanic remained a glowing beacon of human achievement, moving through the night with the power of converted steam.
Lighting the Way: The Titanic's Electrical Illumination
The Titanic's opulent interiors were significantly enhanced by its advanced electrical lighting system, which not only underscored the ship's luxury but also demonstrated the technological marvels of the age. With more than 10,000 light bulbs illuminating its spaces, the Titanic offered an unprecedented level of brightness and comfort, unseen in most places around the world at the time. The extensive use of electric lights was a testament to the ship's innovative design, highlighting its grandeur and the ambitious vision behind its construction.
The ship's lighting scheme was carefully designed to create an atmosphere of warmth and elegance. From the grand dining rooms to the intimate lounges, each area was bathed in light that accentuated its decorative details and luxury appointments. This meticulous attention to lighting helped to forge a memorable experience for the passengers, making the interiors feel more welcoming and luxurious. The electric lights also played a crucial role in the functionality of the ship, ensuring that public spaces, corridors, and cabins were well-lit, thereby enhancing safety and navigation onboard for both passengers and crew.
A notable feature of the Titanic's electrical lighting was its variety. The ship boasted an array of lighting fixtures, from ornate chandeliers in the first-class areas to more practical but still aesthetically pleasing lamps in the second and third-class sections. This diversity not only catered to the different needs and tastes of its passengers but also showcased the versatility of electric lighting as a design element.

Moreover, the implementation of electric lighting on the Titanic was a forward-thinking approach that marked a departure from the more traditional use of gas and oil lamps on ships. This transition to electricity reduced the risk of fires, a common hazard with gas lighting, and allowed for greater control over the lighting levels, further enhancing passenger comfort.
The illumination of the Titanic with electric lights was a clear indicator of the ship's modernity and luxury. It reflected the period's optimism in technological progress and the belief that human ingenuity could conquer natural elements. As passengers moved through the ship's beautifully lit spaces, they were part of a moment in history where the marvels of electricity were just beginning to touch the edges of everyday life, making the Titanic a shining example of what the future held.
A Look at the Ship's Electricity Consumption
Exploring the Titanic's electricity consumption unveils the monumental scale at which the ship operated. Its trio of electric generators tirelessly converted steam into electrical power, driving a system that was nothing short of revolutionary for its time. These generators fed into an intricate network that distributed electricity to every corner of the ship, powering an array of amenities and operations that demanded a significant amount of energy.
Given the Titanic's vast array of electrical applications—from over 10,000 light bulbs to electric heaters, fans, and the ship's pioneering elevators—it's clear that the ship's electricity consumption was colossal. The precise amount of electricity consumed by the Titanic during its voyage is hard to quantify, but it undoubtedly set a new benchmark for energy use at sea. This was a ship that, beyond mere transportation, offered a glimpse into a future where electric power could provide unprecedented levels of comfort and luxury.
Electricity on the Titanic wasn't just about illumination and warmth; it also powered the ship's communication systems, such as the Marconi wireless telegraph, which was essential for sending messages across the Atlantic. This, combined with the operation of crucial navigational equipment, added further to the ship's electrical load.
The engineering feat of generating and distributing such vast amounts of electricity on a moving vessel speaks to the ingenuity and forward-thinking of the time. The Titanic's engineers monitored and managed this consumption with a meticulous eye, ensuring that the balance between efficiency and luxury was always maintained. Their efforts underscored a pivotal shift in maritime history, where the reliance on electricity became a defining feature of modern ship design.
The electrical consumption of the Titanic highlights not only the ship's grandeur and technological prowess but also the era's ambitious embrace of electrical power. It marked a period where electricity began to shape the very fabric of society, promising new horizons of convenience and innovation, with the Titanic serving as a floating testament to this technological optimism.
Comfort and Convenience: Electrical Amenities on the Titanic
Beyond its architectural grandeur and the technological prowess of its electrical system, the Titanic was renowned for the unparalleled level of comfort and convenience it offered to its passengers. This was made possible through an array of electrical amenities that, at the time, represented the height of luxury and innovation. Among these, electric heaters installed in the cabins provided a cozy warmth that countered the chilly Atlantic air, ensuring passengers experienced comfort irrespective of the outside weather. This was particularly appreciated during the nighttime or in colder weather conditions, illustrating the ship's commitment to passenger comfort at all times.

Additionally, the Titanic featured electric fans in its public areas, a thoughtful inclusion that catered to the comfort of its passengers by circulating air and reducing stuffiness in crowded spaces. This was especially crucial given the varying number of people that congregated in these areas, demonstrating the ship's forward-thinking approach to passenger experience.
Perhaps one of the most talked-about electrical amenities aboard the Titanic were its electric elevators. A rarity at the time, especially on a ship, these elevators provided easy and quick access between decks, eliminating the need for passengers to navigate the stairs. This feature was not only a nod towards luxury but also accessibility, allowing all passengers, regardless of their physical capabilities, to move freely and enjoy the ship's numerous facilities. The inclusion of electric elevators underscored the Titanic's reputation as a floating palace, equipped with conveniences that were ahead of its time.
These amenities, powered by the ship's robust electrical system, were not just about adding touches of luxury; they were integral to the Titanic's vision of redefining travel at sea. They showcased the potential of electric power in enhancing the quality of life, even in the middle of the ocean. Through these electrical conveniences, the Titanic demonstrated an unprecedented commitment to passenger comfort, setting new standards for maritime travel that would influence the design and operation of ships for decades to come.
The Engine Room: Where Coal Met Current
Nestled deep within the bowels of the Titanic, the engine room was a labyrinth of machinery and bustling activity, a place where the raw energy of coal was transformed into the electrical current that powered the ship's many innovations. This was the domain of the stokers and engineers, whose Herculean efforts ensured the smooth operation of the vessel's heart. Here, coal was shoveled into massive furnaces, heating water to create steam that, in turn, drove the enormous electric generators responsible for supplying the ship with power.
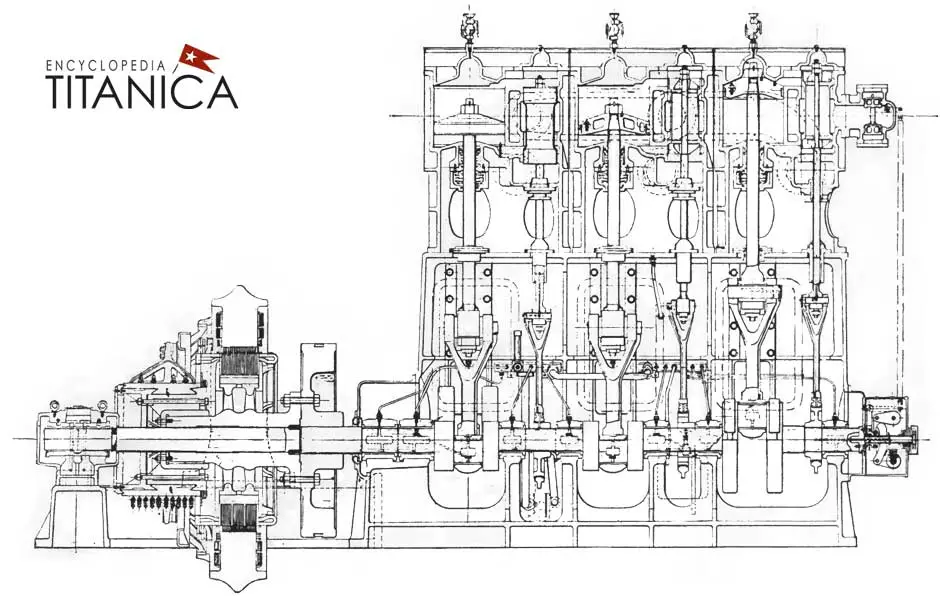
This continuous, demanding process required a precise orchestration of manpower and machinery. The engine room's environment was intense, with the heat from the furnaces and the noise from the machinery creating challenging conditions for the crew. Yet, it was within this challenging environment that the Titanic's electrical power was born. The conversion of coal into steam and then into electrical energy was a marvel of the era, showcasing the industrial might and technological advancements of the time.
Key to this process were the ship's boilers, which numbered 29 in total, each playing a crucial role in steam production. The steam generated by these boilers not only propelled the ship across the Atlantic but also powered the dynamos, the ship's electric heart, generating the electricity needed for everything from lighting to communication systems.
The engine room's strategic importance was underscored by its design and the rigorous work ethic of those who manned it. Despite the harsh conditions, the engineers and stokers maintained a relentless pace, their efforts ensuring that passengers above enjoyed a level of luxury and comfort powered by the unseen but vital energy conversion taking place below deck.
In this coal-fired crucible, the foundations of modern maritime electrical systems were laid, with the Titanic serving as a monumental example of how traditional energy sources like coal could be harnessed to fuel the technological advancements that defined the early 20th century.
Electrical Engineers of the Titanic
Onboard the RMS Titanic, a cadre of highly skilled electrical engineers played an essential role in the smooth operation of the ship's pioneering electrical systems. Tasked with the continuous, efficient running of the electric generators, these professionals were the unsung heroes who worked tirelessly behind the scenes. Their work ensured that the Titanic's vast array of electrical amenities and navigational systems functioned without a hitch, contributing significantly to the comfort and safety of everyone on board.
These engineers possessed a deep understanding of the cutting-edge technology of their time, a necessity given the complexity and scale of the Titanic's electrical infrastructure. They were responsible for monitoring the output of the ship's dynamos, making precise adjustments to accommodate the fluctuating demand for electricity throughout the voyage. Their expertise extended to troubleshooting and repairing any electrical malfunctions that might arise, tasks that required not only technical knowledge but also quick thinking and resourcefulness.
Operating within the engine room's challenging environment, amidst the roar of machines and the heat from the boilers, these engineers demonstrated remarkable dedication. Their round-the-clock vigilance was crucial, especially considering the Titanic's reliance on electricity for lighting, heating, communication, and even life-saving signals. The electrical engineers' ability to maintain a steady supply of power was, therefore, vital for both the ship's operational efficiency and the welfare of its passengers and crew.
In an age where the potential of electrical engineering was just beginning to be fully realized, the electrical engineers aboard the Titanic were at the forefront of this technological revolution. Their work not only underscored the importance of electricity in modern maritime travel but also set new standards for future generations of engineers. Through their efforts, the Titanic was able to offer an unprecedented level of luxury and safety, making it a floating showcase of human ingenuity and the transformative power of electricity.
Safety and Signals: The Electrical Systems in Emergencies
During times of crisis, the Titanic's sophisticated electrical system became an essential tool for safety and communication. Equipped with cutting-edge technology, the ship utilized its electrical capabilities to facilitate urgent signaling and maintain vital links, both within the vessel and to the outside world. Among these technologies was the Marconi wireless telegraph system, an innovative use of electrical communication that allowed the Titanic to send distress signals over great distances. This system played a pivotal role during the Titanic's final hours, as it was used to transmit SOS messages that ultimately led to the rescue of some survivors.
Additionally, the ship's electrical infrastructure supported an array of alarm systems designed to quickly alert crew and passengers to danger. These alarms, reliant on the continuous operation of the ship's electric generators, were critical for initiating emergency protocols. Electric signal lights and illuminated emergency exit signs further leveraged the Titanic's electrical prowess to guide passengers towards safety during the chaos that followed the iceberg collision.
The electrical engineers, tasked with the maintenance and operation of the Titanic's generators and electrical systems, were also instrumental in emergency situations. Their expertise ensured that power was directed to essential communication and safety systems when it mattered most. The redundancy built into the Titanic's electrical design, with multiple generators and circuits, was intended to provide a layer of safety by ensuring that a failure in one component wouldn't result in a total loss of power.
However, despite these precautions, the tragic outcome of the Titanic underscores the limitations of even the most advanced technology of the time when faced with nature's unpredictability. The use of electricity for emergency signaling and communication on the Titanic set a precedent, highlighting the importance of electrical systems in maritime safety and paving the way for future advancements in ship design and emergency protocols.
The Role of Electricity During the Sinking
As the Titanic met its tragic fate, the role of electricity during the sinking became a crucial element in the unfolding drama. With the iceberg collision compromising the ship's hull, the electrical systems played a key part in the immediate aftermath.
Despite the severe damage, the Titanic’s generators continued to function for some time, providing much-needed power for lighting and essential communication systems. This allowed for distress signals to be sent out via the Marconi wireless system, which was instrumental in calling for help and coordinating rescue efforts. Inside the ship, electric lighting helped maintain a semblance of order amid growing panic, guiding passengers to safety routes and lifeboats.
The persistence of electrical power under such dire circumstances underscored the resilience of the Titanic’s engineering but also highlighted the importance of having reliable electrical systems in emergencies. However, as water flooded the engine rooms, the eventual loss of power plunged the Titanic into darkness, signaling the final moments of the ship's tragic journey.
The Legacy of Titanic's Electrical System
The sinking of the Titanic not only marked one of the most infamous maritime tragedies but also served as a catalyst for sweeping changes within the maritime industry, particularly in the realms of ship safety and electrical engineering. The electrical system of the Titanic, a pioneering feat for its time, showcased the immense potential and the critical importance of robust electrical design and safety mechanisms in modern shipbuilding.
In the wake of the disaster, maritime safety standards saw significant enhancements, with a particular focus on the electrical systems that power ships' safety and communication equipment. The International Convention for the Safety of Life at Sea (SOLAS), established in 1914, just two years after the Titanic tragedy, was a direct consequence of the disaster. It introduced stringent regulations that mandated better electrical backup systems and emergency power for critical communications and lighting, ensuring that ships could maintain vital functions in the face of adversity.
Furthermore, the Titanic's reliance on its state-of-the-art electrical system, from the Marconi wireless telegraph to its elaborate lighting and heating, underscored the need for reliability and redundancy in electrical design. Lessons from the Titanic have led to the implementation of more sophisticated and fail-safe electrical systems in ships, systems capable of withstanding severe conditions and preventing total power failures. Modern vessels are equipped with multiple independent backup systems and advanced diagnostics to prevent and quickly address electrical faults, a direct nod to the lessons learned from the Titanic's fate.
The legacy of the Titanic's electrical system also extends to the broader field of electrical engineering. The tragedy highlighted the paramount importance of electrical engineers in ensuring the safety and efficiency of maritime operations. Today, electrical engineers are at the forefront of designing innovative solutions that enhance safety, comfort, and sustainability on board ships, drawing inspiration from the pioneering spirit of those who equipped the Titanic.
As such, the Titanic's electrical system, with its ambitious scale and tragic vulnerabilities, has left a lasting imprint on maritime practices. It reminds us of the relentless push towards innovation, balanced with the sobering responsibility of safeguarding lives through rigorous attention to safety and resilience in design.
Summary
The RMS Titanic, a symbol of early 20th-century engineering prowess, embraced electricity as a cornerstone of its operational and luxury features, illustrating the ship's revolutionary approach to maritime travel. With its advanced electric generators, the Titanic managed to illuminate more than 10,000 light bulbs and power an array of amenities, from elevators to heating systems, marking a significant leap in the use of electrical technology aboard passenger liners. The ship's electrical system, a complex network designed for efficiency and safety, underscored the era's optimism in technological progress and human ingenuity's potential to conquer natural elements.
Electrical engineers on the Titanic played a pivotal role, ensuring the seamless operation of this sophisticated system. Their expertise and round-the-clock diligence were instrumental in maintaining the comfort and safety of those onboard, demonstrating the critical importance of electrical engineering in maritime operations. The tragic sinking of the Titanic, while a monumental disaster, catalyzed significant advancements in maritime safety and electrical engineering standards. It highlighted the necessity for stringent safety protocols and the implementation of fail-safe electrical systems to prevent similar catastrophes.
The legacy of the Titanic's electrical system transcends its time, influencing modern ship design and the broader field of electrical engineering. It serves as a reminder of the balance between innovation and safety, inspiring continuous improvement in the design and operation of maritime vessels. As we reflect on the Titanic's story, it's clear that the ship's encounter with destiny has propelled an enduring commitment to enhancing safety and technological prowess in the maritime industry, ensuring that the luxury and innovation it represented continue to evolve in today's engineering feats.
Also read:





